Hey guys! Welcome to another interesting episode on the Diary of a Financial Data Scientist.
The topic I am about to delve into is one that I just successfully conquered last week while working on a project. As a beginner in data science, I had challenges working with codes and applying theoretical knowledge to creating these codes. But, the good news is: I found an amazing way out and it has been an exhilarating experience.
So, sit back, and please pay close attention while I walk you through the essentials of regression analysis.
WHAT IS REGRESSION ANALYSIS?
Regression Analysis is a modeling technique which is used to estimate the relationship between two variables: the dependent and independent variable. The dependent variable may also be referred to as the target variable while the independent variable may be referred to as the predictor variable.
As is the norm in basic mathematics, the independent variable is used to predict or ascertain the value of the dependent variable.
CATEGORIES OF REGRESSION ANALYSIS
The relationship between a target and predictor variable could be categorized in two ways:
Straight Line Regression: This is also known as the linear regression (which will be fully treated shortly) and it expresses the relationship between one predictor variable and one target variable.
Polynomial Curve/ Non-Linear/ Multiple Regression: This is a regression analysis that examines the relationship between one dependent or target variable and two or more predictor or independent variables.
STEPS INVOLVED IN REGRESSION ANALYSIS
There are basic steps that must be observed when regression analysis is being carried out between two variables or among several variables. These steps are highlighted below:
Identifying the Target and the Predictors - As stated earlier, the major reason for regression analysis is to discover the relationship between two or more variables. Hence, it is crucial that the variables to be used in igniting this process are identified first. Once we have successfully identified our dependent and independent variables, the other steps can follow.
Finding the Relationship between the Variables - This is a no-brainer. After identifying the variables needed for our regression analysis exercise, the next procedure is to find out whether or not these variables are even in any way related to one another. It is imperative that relationship(s) exist among these variables else, we would only be crowding our regression model with unnecessary noise.
Estimating the Likely Coefficients - The coefficients of a regression model help us determine the values of the variables used for the regression analysis and ultimately, our final result. It is based on this result that we make predictions and further recommendations. The coefficients are an integral part of every regression analysis without which we cannot make any sense of our regression model.
Finding the Predicted Values of the Target - The predicted values are derived from the coefficients present in our model and with them, we can present our results and make recommendations.
Evaluating the Accuracy of the Relationship - Regression analysis is an iterative process that does not end after all steps have been executed once. Based on the logic behind a regression model, we need to find the relationship that exists among variables but we are not seeking just any existent relationship but the best one. Thus, to do this, we execute all steps over and over again till we achieve that single relationship that fully optimizes the regression model.
Without further ado, let us examine the different types of regression which can be useful for our analysis.
TYPES OF REGRESSION
There are various regression techniques but the technique to be employed depends on:
The shape of the regression line;
The type of dependent or target variable; and
The number of independent variables.
Four types of regression analysis will be treated here and they are highlighted as follows:
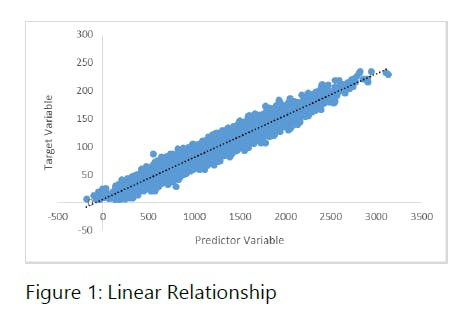
Linear Regression
This is by far the simplest and most commonly used form of regression. Linear regression defines the relationship between only two variables in a regression model with a straight line. This line which defines the relationship between the two variables is also known as the Line of Best Fit. The linear regression equation is given below:
Y = a + bx + e
where Y = the target variable or output
a = the intercept
b = the slope
e = the error term or the bias
x = the input
Logistic Regression
This is a technique used to explain the relationship between one dependent, binary variable, and more than one predictor or independent variable. Simply put, it is a tool essential when dealing with a multiple regression model.
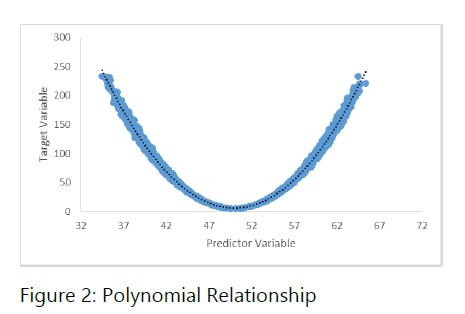
Polynomial Regression
A polynomial regression equation is one whose power of the independent variable is greater than 1. Hence, the line of best fit is not a straight line. The relationship is expressed with the equation:
Y = a + bx + cx^2
Ridge Regression
This is a regression technique used for analyzing multiple regression data suffering from multicollinearity. Multicollinearity occurs where two or more explanatory or predictor variables within a model are highly related. Ridge regression helps to add a degree of bias to the estimates, reduce standard errors, and invariably, give more reliable estimates.
SUMMARY
Regression Analysis helps us to determine the impact of one or more independent variables on a single target variable i.e. how a dependent variable is affected if one or more of the independent variables change.
There are two categories of regression: the linear regression - whose relationship is expressed by a straight line - and the multiple or polynomial regression - whose line of best fit is expressed as a curve.
There are five basic (and iterative) steps needed for a successful regression analysis process.
There are four major types of regression techniques: the linear regression, polynomial regression, ridge regression, and logistic regression.
CONCLUSION
This article has introduced you to the basics of regression analysis and by now, you should be comfortable with looking at fundamental topics in this aspect. In the next article, we would dive deeper into the process of determining the line of best fit, the tools used for this purpose as well as the basic assumptions that guide every regression analysis.
In the meantime, you can take a look at my Regression Analysis project here:
github.com/Tess-hacker/Hamoye-Quiz-2
Don't forget to leave your likes and comments after reading. Would love to hear from you. Till next time.
Thanks for reading!

